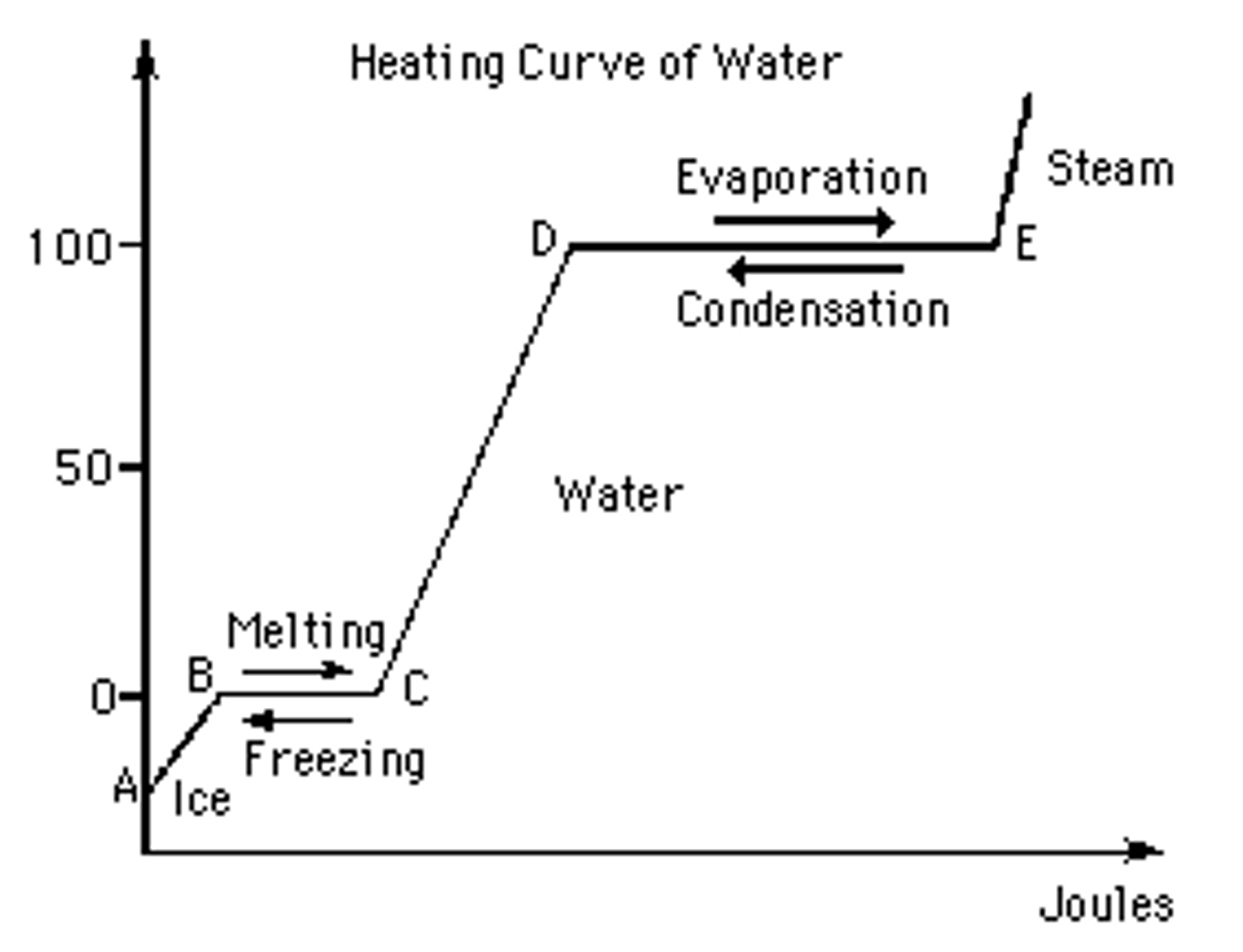
Solid Liquid Gas Melting Point Boiling Point . The melting point of a solid is the same as the freezing point of the liquid. In figure \(\pageindex{2b}\) point a is located at p = 1 atm and t = −1.0°c, within the solid (ice) region of the phase diagram. the melting point of ice is 0oc 0 o c. the melting point is the temperature at which the substance goes from a solid to a liquid (or from a liquid to a solid). Must be transferred, by heating, to a substance for. heat, cool and compress atoms and molecules and watch as they change between solid, liquid and gas phases. The boiling point is the. pure, crystalline solids have a characteristic melting point, the temperature at which the solid melts to become a liquid. the decrease in volume (and corresponding increase in density) is smaller for a solid or a liquid than for a gas, but it is sufficient to melt some of the ice.
from exorgxbax.blob.core.windows.net
the decrease in volume (and corresponding increase in density) is smaller for a solid or a liquid than for a gas, but it is sufficient to melt some of the ice. The melting point of a solid is the same as the freezing point of the liquid. The boiling point is the. the melting point is the temperature at which the substance goes from a solid to a liquid (or from a liquid to a solid). the melting point of ice is 0oc 0 o c. In figure \(\pageindex{2b}\) point a is located at p = 1 atm and t = −1.0°c, within the solid (ice) region of the phase diagram. pure, crystalline solids have a characteristic melting point, the temperature at which the solid melts to become a liquid. Must be transferred, by heating, to a substance for. heat, cool and compress atoms and molecules and watch as they change between solid, liquid and gas phases.
Heating Curve Graph Fusion at Stephen Cooks blog
Solid Liquid Gas Melting Point Boiling Point the decrease in volume (and corresponding increase in density) is smaller for a solid or a liquid than for a gas, but it is sufficient to melt some of the ice. In figure \(\pageindex{2b}\) point a is located at p = 1 atm and t = −1.0°c, within the solid (ice) region of the phase diagram. pure, crystalline solids have a characteristic melting point, the temperature at which the solid melts to become a liquid. The boiling point is the. the melting point is the temperature at which the substance goes from a solid to a liquid (or from a liquid to a solid). The melting point of a solid is the same as the freezing point of the liquid. the decrease in volume (and corresponding increase in density) is smaller for a solid or a liquid than for a gas, but it is sufficient to melt some of the ice. Must be transferred, by heating, to a substance for. the melting point of ice is 0oc 0 o c. heat, cool and compress atoms and molecules and watch as they change between solid, liquid and gas phases.
From general.chemistrysteps.com
Entropy and State Change Chemistry Steps Solid Liquid Gas Melting Point Boiling Point heat, cool and compress atoms and molecules and watch as they change between solid, liquid and gas phases. In figure \(\pageindex{2b}\) point a is located at p = 1 atm and t = −1.0°c, within the solid (ice) region of the phase diagram. The boiling point is the. the melting point is the temperature at which the substance. Solid Liquid Gas Melting Point Boiling Point.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Physical and Chemical Properties PowerPoint Presentation, free Solid Liquid Gas Melting Point Boiling Point the melting point of ice is 0oc 0 o c. Must be transferred, by heating, to a substance for. pure, crystalline solids have a characteristic melting point, the temperature at which the solid melts to become a liquid. the melting point is the temperature at which the substance goes from a solid to a liquid (or from. Solid Liquid Gas Melting Point Boiling Point.
From general.chemistrysteps.com
Boiling Point Elevation Chemistry Steps Solid Liquid Gas Melting Point Boiling Point the melting point is the temperature at which the substance goes from a solid to a liquid (or from a liquid to a solid). In figure \(\pageindex{2b}\) point a is located at p = 1 atm and t = −1.0°c, within the solid (ice) region of the phase diagram. heat, cool and compress atoms and molecules and watch. Solid Liquid Gas Melting Point Boiling Point.
From imgbin.com
Boiling Point Melting Point Heat Temperature Chemistry PNG, Clipart Solid Liquid Gas Melting Point Boiling Point Must be transferred, by heating, to a substance for. In figure \(\pageindex{2b}\) point a is located at p = 1 atm and t = −1.0°c, within the solid (ice) region of the phase diagram. heat, cool and compress atoms and molecules and watch as they change between solid, liquid and gas phases. the decrease in volume (and corresponding. Solid Liquid Gas Melting Point Boiling Point.
From stewartjerry.blogspot.com
22+ Phase Diagram Boiling Point StewartJerry Solid Liquid Gas Melting Point Boiling Point heat, cool and compress atoms and molecules and watch as they change between solid, liquid and gas phases. Must be transferred, by heating, to a substance for. the decrease in volume (and corresponding increase in density) is smaller for a solid or a liquid than for a gas, but it is sufficient to melt some of the ice.. Solid Liquid Gas Melting Point Boiling Point.
From shaunmwilliams.com
Chapter 11 Presentation Solid Liquid Gas Melting Point Boiling Point The boiling point is the. pure, crystalline solids have a characteristic melting point, the temperature at which the solid melts to become a liquid. the melting point of ice is 0oc 0 o c. In figure \(\pageindex{2b}\) point a is located at p = 1 atm and t = −1.0°c, within the solid (ice) region of the phase. Solid Liquid Gas Melting Point Boiling Point.
From schematicnalematiqb.z21.web.core.windows.net
Phase Diagram For One Component System Solid Liquid Gas Melting Point Boiling Point The boiling point is the. heat, cool and compress atoms and molecules and watch as they change between solid, liquid and gas phases. the decrease in volume (and corresponding increase in density) is smaller for a solid or a liquid than for a gas, but it is sufficient to melt some of the ice. In figure \(\pageindex{2b}\) point. Solid Liquid Gas Melting Point Boiling Point.
From wiringdiagramidealless.z21.web.core.windows.net
How To Read A Phase Change Diagram Solid Liquid Gas Melting Point Boiling Point The melting point of a solid is the same as the freezing point of the liquid. pure, crystalline solids have a characteristic melting point, the temperature at which the solid melts to become a liquid. the decrease in volume (and corresponding increase in density) is smaller for a solid or a liquid than for a gas, but it. Solid Liquid Gas Melting Point Boiling Point.
From www.britannica.com
Melting point Definition & Facts Britannica Solid Liquid Gas Melting Point Boiling Point the decrease in volume (and corresponding increase in density) is smaller for a solid or a liquid than for a gas, but it is sufficient to melt some of the ice. heat, cool and compress atoms and molecules and watch as they change between solid, liquid and gas phases. The melting point of a solid is the same. Solid Liquid Gas Melting Point Boiling Point.
From thepiquelab.com
Tackling Heat Energy Questions Melting & Boiling Points! Primary Solid Liquid Gas Melting Point Boiling Point Must be transferred, by heating, to a substance for. heat, cool and compress atoms and molecules and watch as they change between solid, liquid and gas phases. the melting point of ice is 0oc 0 o c. In figure \(\pageindex{2b}\) point a is located at p = 1 atm and t = −1.0°c, within the solid (ice) region. Solid Liquid Gas Melting Point Boiling Point.
From www.expii.com
Phase Change Diagram of Water — Overview & Importance Expii Solid Liquid Gas Melting Point Boiling Point In figure \(\pageindex{2b}\) point a is located at p = 1 atm and t = −1.0°c, within the solid (ice) region of the phase diagram. pure, crystalline solids have a characteristic melting point, the temperature at which the solid melts to become a liquid. Must be transferred, by heating, to a substance for. heat, cool and compress atoms. Solid Liquid Gas Melting Point Boiling Point.
From schematicviciosinfin17.z22.web.core.windows.net
How To Make A Phase Diagram Solid Liquid Gas Melting Point Boiling Point Must be transferred, by heating, to a substance for. The melting point of a solid is the same as the freezing point of the liquid. The boiling point is the. the melting point is the temperature at which the substance goes from a solid to a liquid (or from a liquid to a solid). the decrease in volume. Solid Liquid Gas Melting Point Boiling Point.
From stock.adobe.com
Boiling and Evaporation, Freezing and Melting Points of Water. Stock Solid Liquid Gas Melting Point Boiling Point heat, cool and compress atoms and molecules and watch as they change between solid, liquid and gas phases. the melting point of ice is 0oc 0 o c. In figure \(\pageindex{2b}\) point a is located at p = 1 atm and t = −1.0°c, within the solid (ice) region of the phase diagram. the melting point is. Solid Liquid Gas Melting Point Boiling Point.
From printablelistquinta.z21.web.core.windows.net
What Is A Heat Curve Solid Liquid Gas Melting Point Boiling Point the melting point is the temperature at which the substance goes from a solid to a liquid (or from a liquid to a solid). In figure \(\pageindex{2b}\) point a is located at p = 1 atm and t = −1.0°c, within the solid (ice) region of the phase diagram. The melting point of a solid is the same as. Solid Liquid Gas Melting Point Boiling Point.
From unistudium.unipg.it
Phase Diagrams Solid Liquid Gas Melting Point Boiling Point pure, crystalline solids have a characteristic melting point, the temperature at which the solid melts to become a liquid. The boiling point is the. The melting point of a solid is the same as the freezing point of the liquid. In figure \(\pageindex{2b}\) point a is located at p = 1 atm and t = −1.0°c, within the solid. Solid Liquid Gas Melting Point Boiling Point.
From www.physicsfox.org
Melting & Boiling • Matter • Physics Fox Solid Liquid Gas Melting Point Boiling Point In figure \(\pageindex{2b}\) point a is located at p = 1 atm and t = −1.0°c, within the solid (ice) region of the phase diagram. the decrease in volume (and corresponding increase in density) is smaller for a solid or a liquid than for a gas, but it is sufficient to melt some of the ice. The boiling point. Solid Liquid Gas Melting Point Boiling Point.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Physical Properties of Water Boiling Point, Melting Point and Solid Liquid Gas Melting Point Boiling Point The melting point of a solid is the same as the freezing point of the liquid. The boiling point is the. the melting point of ice is 0oc 0 o c. pure, crystalline solids have a characteristic melting point, the temperature at which the solid melts to become a liquid. the decrease in volume (and corresponding increase. Solid Liquid Gas Melting Point Boiling Point.
From exorgxbax.blob.core.windows.net
Heating Curve Graph Fusion at Stephen Cooks blog Solid Liquid Gas Melting Point Boiling Point the melting point is the temperature at which the substance goes from a solid to a liquid (or from a liquid to a solid). the decrease in volume (and corresponding increase in density) is smaller for a solid or a liquid than for a gas, but it is sufficient to melt some of the ice. The boiling point. Solid Liquid Gas Melting Point Boiling Point.